Need Clomid? Focus your search on reputable online pharmacies with verified licenses and positive customer reviews. Avoid sites offering suspiciously low prices or lacking transparent contact information.
Check for secure payment gateways (look for HTTPS) and verify the pharmacy’s registration with relevant regulatory bodies. Confirm their commitment to patient privacy and data security through their privacy policy.
Remember, obtaining medication without a prescription carries risks. Prioritize consulting a doctor before using Clomid, regardless of the source. A healthcare professional can assess your specific needs and advise on safe dosage and potential side effects. They can also help you navigate potential interactions with other medications you might be taking.
Always prioritize your health. Thoroughly investigate any pharmacy before making a purchase, comparing prices and services across multiple trustworthy sites.
Disclaimer: This information is for guidance only and does not constitute medical advice. Consult a healthcare professional before using any medication.
- Free Clomid: A Comprehensive Guide
- Patient Assistance Programs
- Free Clinics and Community Health Centers
- Government Assistance Programs
- Negotiating with Pharmacies
- Important Note:
- Understanding Clomid and its Uses
- The Risks and Side Effects of Clomid
- Common Side Effects
- Less Common but Serious Risks
- Understanding the Risks: A Summary
- Before You Start
- Finding Legitimate Sources for Clomid: Dispelling Myths about “Free” Medications
- Understanding the Risks of Counterfeit Clomid
- Legitimate Avenues for Obtaining Clomid
- The Importance of Medical Supervision with Clomid
- Affordable Alternatives to Clomid: Exploring Treatment Options
- Lifestyle Modifications & Supplements
- Alternative Medications & Procedures
- Important Note:
- Navigating Insurance Coverage for Fertility Treatments
- Legal Considerations and the Dangers of Counterfeit Clomid
- Counterfeit Clomid: A Serious Threat
- Protecting Yourself
- Reporting Suspicious Activity
Free Clomid: A Comprehensive Guide
Finding free Clomid requires careful consideration. Insurance coverage varies widely. Contact your insurance provider directly to confirm your coverage. Many insurance plans require pre-authorization before covering Clomid. This process can involve paperwork and physician consultations.
Patient Assistance Programs
Several pharmaceutical companies offer patient assistance programs (PAPs). These programs provide free or discounted medications to eligible patients. Eligibility criteria generally involve income restrictions. Each program has unique application processes; research the manufacturer’s website for specific details. Check eligibility requirements carefully before applying.
Free Clinics and Community Health Centers
Some free or low-cost clinics provide medications, including Clomid, to patients in need. Locate nearby clinics through online searches or by contacting your local health department. Eligibility often depends on financial need and residency requirements. Remember to confirm their services and availability before visiting.
Government Assistance Programs
Government programs may offer medication assistance in certain circumstances. Contact your local social services agency for information regarding relevant programs in your area. Income limitations usually apply for eligibility. Program availability and guidelines fluctuate, so regular checks are recommended.
Negotiating with Pharmacies
Pharmacies may offer discounts or payment plans. Directly discuss your financial situation with the pharmacist. Some pharmacies participate in manufacturer coupon programs that can significantly lower the cost. Explore all available options.
Important Note:
Always consult a physician before starting or changing any medication, including Clomid. Self-medicating can have serious health consequences. This information is for guidance only, not medical advice.
Understanding Clomid and its Uses
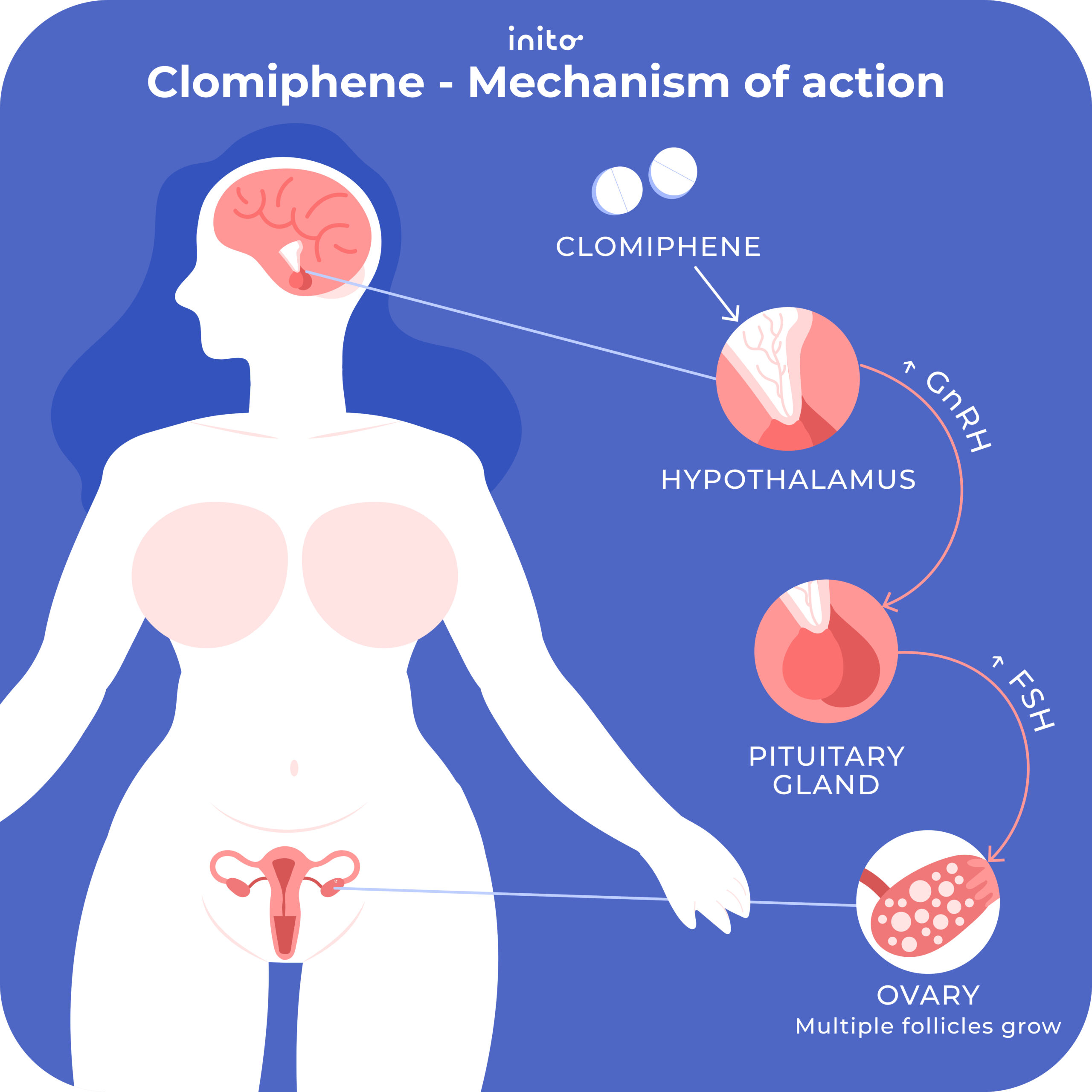
Clomid, or clomiphene citrate, is a medication primarily used to stimulate ovulation in women. It works by blocking estrogen receptors in the hypothalamus and pituitary gland, leading to increased production of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). These hormones are crucial for egg development and release.
Infertility Treatment: Clomid’s main application is treating infertility caused by anovulation (failure to ovulate). Doctors often prescribe it for women with irregular menstrual cycles or those who haven’t conceived after trying for a year. The typical course involves daily doses for 5 days, often starting on cycle day 3 or 5. Your doctor will adjust the dosage based on your individual response.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): Clomid effectively helps women with PCOS, a hormonal disorder characterized by infrequent or absent ovulation. By stimulating ovulation, it improves the chances of pregnancy. However, response varies, and some women may require alternative treatments.
Important Note: Clomid isn’t a guaranteed path to pregnancy. Multiple cycles may be needed, and success rates depend on factors like age and overall health. Some women experience side effects like hot flashes, mood swings, and visual disturbances. Always discuss potential risks and benefits with your physician before starting treatment.
Male Infertility: In men, Clomid sometimes aids in improving sperm production. However, its use in male infertility is less common than in women. This application usually involves a specialist and is subject to specific conditions.
Off-Label Uses: While not officially approved, Clomid is sometimes used to enhance fertility in men undergoing assisted reproductive technologies. Remember, this is off-label use, and its efficacy and safety are not as thoroughly researched.
Finding a Doctor: If you’re considering Clomid, consult a reproductive endocrinologist or fertility specialist. They can accurately assess your situation, determine if Clomid is appropriate for you, and guide you throughout the process. They will monitor your response to treatment and adjust your medication plan as necessary.
The Risks and Side Effects of Clomid
Clomid, while helpful for some, carries potential risks. Understand these before considering use. Consult your doctor immediately if you experience any concerning symptoms.
Common Side Effects
Many women experience mild side effects. These include hot flashes, headaches, mood swings, and bloating. These usually subside as your body adjusts. Severe bloating might indicate ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS), a serious complication requiring medical attention.
Less Common but Serious Risks
Multiple pregnancies (twins, triplets, etc.) are a possibility. This increases risks during pregnancy and delivery. Ovarian cysts, though usually benign, can cause pain and require monitoring. Visual disturbances, such as blurred vision, are another potential side effect and need immediate medical attention. Rarely, Clomid is associated with a slightly increased risk of certain types of cancer, although the evidence is not conclusive.
Understanding the Risks: A Summary
| Side Effect | Frequency | Severity | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hot flashes, headaches, mood swings | Common | Mild | Monitor, discuss with doctor if bothersome |
| Bloating, ovarian cysts | Less common | Variable | Seek medical advice if severe or persistent |
| Multiple pregnancy | Possible | Significant | Careful monitoring throughout pregnancy |
| Visual disturbances | Rare | Serious | Immediate medical attention required |
Before You Start
Thorough pre-treatment discussions with your doctor are crucial. Your doctor will assess your medical history, perform tests, and discuss potential benefits and risks tailored to your situation. Open communication is key to a safe and informed treatment plan.
Finding Legitimate Sources for Clomid: Dispelling Myths about “Free” Medications
Seek Clomid only through a licensed healthcare professional. This ensures you receive a proper diagnosis, personalized dosage, and monitoring for potential side effects. Never purchase medication from unverified online pharmacies or individuals offering “free” Clomid. These sources often sell counterfeit drugs, posing significant health risks.
Understanding the Risks of Counterfeit Clomid
Counterfeit Clomid may contain incorrect dosages, harmful contaminants, or even be completely inactive. This can lead to treatment failure, delayed diagnosis, and serious health complications. Always prioritize your safety and health by obtaining medication through legitimate channels.
Legitimate Avenues for Obtaining Clomid
Your primary care physician or a reproductive endocrinologist can prescribe Clomid after a thorough evaluation. They will determine if Clomid is appropriate for your individual circumstances and monitor your progress. Insurance coverage may be available, reducing the overall cost. Explore your insurance options and discuss potential financial assistance programs with your healthcare provider.
The Importance of Medical Supervision with Clomid
See a doctor before using Clomid. This isn’t optional; it’s vital for your health and the success of treatment.
Clomid, while effective for some, carries potential risks. Your doctor will assess your suitability, considering factors like:
- Your medical history: Pre-existing conditions like ovarian cysts or uterine fibroids affect treatment.
- Your reproductive health: Regular cycle monitoring helps determine the appropriate dosage and treatment duration.
- Your overall health: Clomid can impact various bodily systems. Your doctor must gauge your health before prescribing it.
Regular monitoring during treatment is crucial. Expect:
- Ultrasound scans to track follicle growth and prevent ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS).
- Blood tests to measure hormone levels and assess your response to Clomid.
- Discussions about potential side effects and strategies to manage them. These include hot flashes, mood swings, and visual disturbances.
Ignoring medical advice can lead to complications. OHSS, for instance, can be serious. Close monitoring minimizes the risk. Your doctor will tailor treatment to your individual needs, adjusting dosage or duration as necessary. This personalized approach increases the chances of successful conception while minimizing potential problems.
Remember: responsible use of Clomid is key. Prioritize your health and follow your doctor’s guidance throughout the process.
Affordable Alternatives to Clomid: Exploring Treatment Options
Consider lifestyle changes first. Weight management, regular exercise, and a balanced diet can significantly improve fertility for some individuals. These adjustments often precede more expensive medical interventions.
Lifestyle Modifications & Supplements
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: BMI within the healthy range is crucial. Consult a doctor or registered dietitian for personalized guidance.
- Regular Exercise: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week.
- Dietary Adjustments: Focus on nutrient-rich foods. Consider supplements like Myo-inositol, which shows promise in improving ovulation, but always consult your doctor before starting any supplements.
If lifestyle changes aren’t sufficient, explore these options:
Alternative Medications & Procedures
- Letrozole: A less expensive medication sometimes used to stimulate ovulation. Your doctor can assess its suitability for you.
- Metformin: Primarily used for diabetes, it can also be beneficial for women with PCOS who are struggling with ovulation.
- Intrauterine Insemination (IUI): A less invasive and often cheaper alternative to IVF, involving placing sperm directly into the uterus.
- Ovulation Tracking: Using ovulation predictor kits (OPKs) can help identify fertile windows, increasing the chances of conception without medication.
Remember, treatment success varies. Open communication with your doctor is paramount to finding the most suitable and affordable path to achieve your family-building goals.
Important Note:
This information is for general knowledge and does not substitute professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or a fertility specialist before making any decisions regarding your treatment plan.
Navigating Insurance Coverage for Fertility Treatments
Check your policy details immediately. Many policies have specific clauses related to fertility treatments. Look for terms like “infertility,” “in vitro fertilization (IVF),” “intrauterine insemination (IUI),” and “egg donation.” These terms define what’s covered, and any limitations or exclusions.
Contact your insurance provider directly. Ask about pre-authorization requirements. Pre-authorization often means submitting a detailed treatment plan before starting any procedure, ensuring coverage. Clarify any specific forms you need to complete.
Understand your plan’s benefit maximums. This specifies the total amount your insurance will cover per year or per lifetime for fertility treatments. Knowing this limit helps you budget appropriately.
Inquire about in-network providers. Using in-network doctors and clinics usually results in lower out-of-pocket costs. Your insurance company can provide a list of participating specialists.
Explore fertility treatment financial assistance programs. Many organizations offer grants or loans to help people afford fertility treatments. Research options based on your circumstances and eligibility.
Maintain meticulous records. Keep copies of all medical bills, insurance claims, and correspondence with your insurance provider. Accurate documentation simplifies disputes or appeals if necessary.
Prepare for potential appeals. If your claim is denied, understand your right to appeal the decision. Carefully review the denial reason and gather additional supporting medical documentation to strengthen your appeal.
Legal Considerations and the Dangers of Counterfeit Clomid
Buying Clomid online without a prescription is illegal in many countries. This includes obtaining “free” Clomid from unregulated sources. Penalties vary, but can include fines and even imprisonment. Remember, your health is at risk too.
Counterfeit Clomid: A Serious Threat
Counterfeit Clomid often contains incorrect dosages of active ingredients or harmful contaminants. This poses significant risks to your reproductive health. Incorrect dosages can lead to ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS), multiple pregnancies, or failure to ovulate. Contaminated drugs may cause severe allergic reactions or other health problems. You may not experience the desired effects and further endanger your wellbeing.
Protecting Yourself
Always obtain Clomid from a licensed physician and a reputable pharmacy. Never purchase medications from unknown online sellers or through informal channels. If you need help affording medication, explore options like patient assistance programs offered by pharmaceutical companies or government subsidies. Confirm the legitimacy of any pharmacy or online seller before ordering any medication. Check their license and contact information. Your health depends on it.
Reporting Suspicious Activity
Report any suspicious online pharmacies or sellers to the appropriate authorities in your country. This helps protect others from potentially harmful products. Contact your local health authorities or relevant regulatory agencies for guidance on reporting processes.